The terms “concrete block” and “cinder block” are commonly used reciprocally; however, they are not the same. While they share some basic characteristics, there are substantial differences between these two building materials. In this write-up, we will check out the distinctions between cinder blocks and concrete blocks to assist you in recognizing their one-of-a-kind buildings and applications.
Cinder Block vs Concrete Block
Here’s a detailed comparison between cinder blocks and concrete blocks:
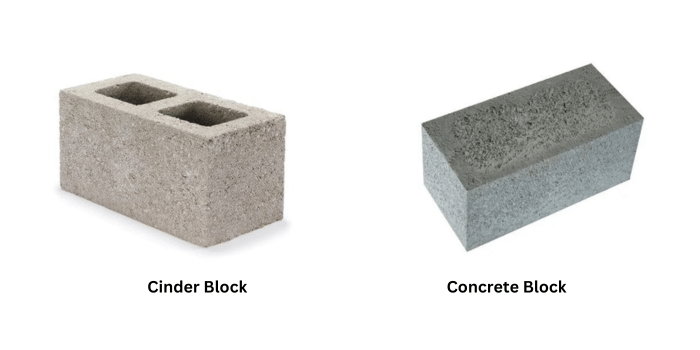
1. Composition
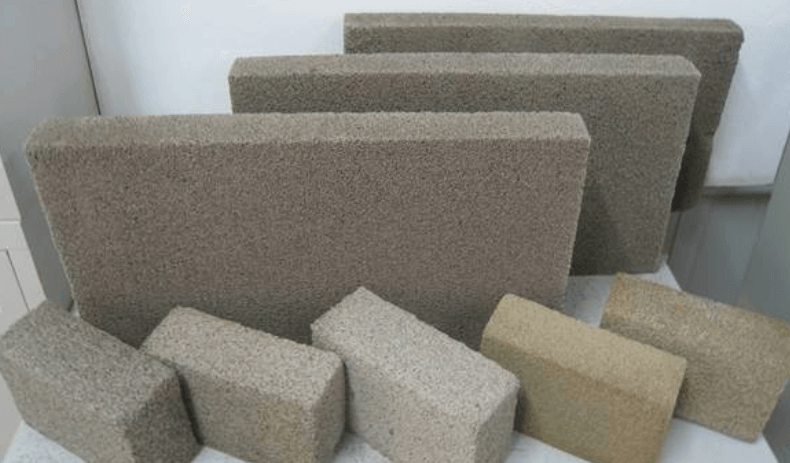
- Cinder Block: Cinder blocks are composed of concrete and coal cinders, which are the remnants of burnt coal. These cinders are used as an aggregate in the block’s construction.
- Concrete Block: Concrete blocks, on the other hand, are primarily made from a mixture of cement, sand, and either crushed stone or sand, depending on the desired strength and density.
2. Structural Design
- Cinder Block: Cinder blocks typically have a hollow rectangle or square structure, which results in them being lighter and less dense compared to concrete blocks.
- Concrete Block: Concrete blocks have a more solid and flattened structure, which makes them denser and heavier than cinder blocks.
3. Strength and Durability
- Cinder Block: Cinder blocks lack significant tensile strength and may not be suitable for load-bearing applications. They are generally less durable compared to concrete blocks.
- Concrete Block: Concrete blocks are known for their hardness and durability. They can withstand higher pressure and are commonly used in load-bearing structures.
4. Flexibility and Building Codes
- Cinder Block: Due to their limited flexibility and lower strength, many building codes restrict or discourage the use of cinder blocks in construction projects.
- Concrete Block: Concrete blocks are much stronger and more versatile, making them a preferred choice in various construction projects. They meet stricter building code requirements.
5. Applications
- Cinder Block: Cinder blocks are often used in smaller-scale projects, such as garden walls, project walls, or decorative elements.
- Concrete Block: Concrete blocks are commonly employed in larger and more substantial construction projects, including residential and commercial buildings, retaining walls, and foundations.
6. Popularity and Production
- Cinder Block: Cinder blocks are considered somewhat old-fashioned and have not been mass-produced for around 50 years.
- Concrete Block: Concrete blocks remain popular in modern construction due to their durability and advantages over cinder blocks.
7. Cost
- Cinder Block: Cinder blocks can be more expensive in the long run because they may require more maintenance and repairs.
- Concrete Block: Concrete blocks are generally more affordable and cost-effective over the life of a structure.
In conclusion, while concrete blocks and concrete blocks might appear comparable initially, their differences in structure, stamina, longevity, and application make them distinct structure products. It’s necessary to consider these aspects when choosing between your building and construction jobs to make certain security and long life.
Keyword phrases: what are concrete blocks made from, cinder block vs cinder block, concrete cinder blocks, cinder blocks vs concrete blocks, cynder block, difference in between concrete block and concrete block, concrete vs concrete block, cinder vs cinder block, is cinder block concrete, cinderblocks, are concrete blocks concrete.